Did you enjoy this post? Sign Up for my newsletter so you won’t miss another article.
Our Attention Span and Money
The average attention span and short-term memory recall has declined over the last ten years. Some say it’s due to our ability to look up anything we need so our brains no longer find it a vital function.
Either way, I have strong memories of 9-11 and the 2008 crash. I can remember exactly where I was, what the room looked like, who was around me, etc. Why do I remember the bad instances so much more?
Human psychology is so much more focused on the bad due to evolution. Those who remembered the poison berries another ate lived longer. Remembering bad moments in great detail allowed us to survive a longer time.
Thanks evolution – you take away my good memories and attention span and leave me with the bad ones?!
So what does this mean for today’s millennials?
We remember what it felt like and what is looked like, but we didn’t know the problems were primarily at home, and not worldwide.
The table below is a great example of how different types of stock (U.S. large stocks, U.S. small stocks, emerging markets, international, real estate, etc) can widely differ in performance from year to year.
Follow the S&P 500 (U.S. large companies stock) for example. In the late 90s the S&P 500 was on a roll, and then when 2000 hit it became one of the worst performers for the year. This chart ends in 2014, but I have a feeling if you saw the last 2 years the S&P 500 would be near the top again.
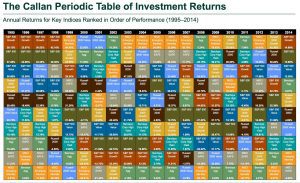
Looking at the changes in this 10 year period of time, I can only imagine how frustrating it must be for new investors. How can you consistently pick the right asset classes for greatest return?
In my mind, you can’t. This is why I believe markets are efficient and few investors can outperform, because it is all priced into the stock over time.
This allows me the freedom to ask: how do I protect and maximize my return while reducing the likeliness of large jumps like the S&P 500 in the above table? I do this by holding a portfolio of many types of stock. When one type dips, I have another that may rise in value or help counteract the effect. Thus providing a more stable return over time.
So what about keeping my money in all cash? There is no risk to that, right?
I am all for maintaining an emergency fund based on your lifestyle and needs in cash. I also believe large expenses in the next few years are better left in cash.
However, I do believe there is a strong argument for investing into the stock market to combat long-term inflation.
Remember when you could get gas in the 90s for less than $1.00? Remember when bread was less than $1.00 and you could scrape together a lunch with the change you found in your parent’s stash?
The changes over the last 20 years are a prime example of what could happen to your cash pile over the next 20-30 years. In fact, we’ve seen inflation every decade since the 1940s and only over the last three years did it momentarily slow down.[1]
Our memories can be fickle friends and keep us from making good long-term decisions. Adding to an already emotional topic – money.
If you are interested in talking to someone about growing your wealth, start now and schedule a time for your free 30 minute consultation with me.
Did you enjoy this post? Sign Up for my newsletter so you won’t miss another article.
The above discussion is for informational purposes only. Recommendations are of a general nature, not based on knowledge of any individual’s specific needs or circumstances, and there is no intent to provide individual investment advisory, supervisory or management services.
______
[1] For more information and a great chart, check out InflationData.com, “Average Annual Inflation Rates by Decade” by Tim McMahon on June 18, 2015
This post was inspired by the article in The New York Times, “Praise Is Fleeting, but Brickbats We Recall” by Alina Tugend: March 23, 2012 and the book Moonwalking with Einstein: The Art and Science of Remembering Everything by Joshua Foer

